At the end of 1937, it
became evident that the French aeronautical industry was not in
a position to supply the Air Force with the modern fighters it
so badly needed. The specifications of the "V" plan seemed utopian,
and it was therefore logically towards foreign countries that
the Air Ministry turned to try to make up for the delay.. Steps
in Europe resulted in the purchase of unsatisfactory aircraft
such as the Koolhoven FK58 Dutch, but only the United States seemed
to be able to meet our need. Unofficial negotiations began at
the end of 1937 to acquire several hundred modern fighters.
At that time the
Curtiss P36 had just been ousted by the Seversky P-35 in the USAAC
equipment contest. The Curtiss P36 becomes Curtiss H75 for export,
which will be chosen by the French services. The negotiations
were rather lengthy: the price of the Curtiss H75 was indeed very
high in comparison with the national productions such as the Morane
MS406 or Bloch MB152, but the tensions in Europe left little choice
to the French emissaries ... A first contract for the purchase
of 100 Curtiss H75 A1 (see "Version") was signed in
May 1938. After testing by French pilots in Buffalo, the first
Curtiss H75 A1, brought back to French standards, are dismantled
in France December 1938. They were directly purchased routed to
the plant of Bourges in charge of assembly. The situation in Europe
is deteriorating after the Munich crisis, and new negotiations
are being launched with the United States to acquire new aircraft.
The Curtiss H81 was chosen as the curtiss P40, but the delivery
delays of the Allison engines of this version led to the choice
of the Curtiss H75 A2, an improved version of the H75 equipped
with a motor and an armament more powerful. A new order of 100
machines has passed ..
In September 1939,
the entire order was honored, and the first fighter Group were
equipped as of March 1939 : GC I / 5, GC II / 5, GC I / 4,. After
the declaration of War, in September 39, France again turns to
the United States for a third command. The context is however
more difficult with a France now in war, the United States now
neutral, and a unit price of Curtiss H75 even higher ... An order
is finally passed for the supply of 530 Curtiss H75 A3, and 100
new Curtiss H81 (P40) now available. The first Curtiss H75 A3
arrives in France in March 1940. Only part of the order can arrive
in time on the national territory: a part sinks at sea, the rest
is diverted to the West Indies to be stored, or Casablanca in
Morocco. As for the H75 A4 version, less than a dozen aircraft
arrive in France, too late to take part in the fighting.
At the signature
of the Armistice, all the Fighter Groups equipped with Curtiss
H75 take refuge in North Africa. TThere are about 186 aircraft,
while 45 others stayed in metropolitan France.The GC I / 4, GC
I / 5 and GC II / 5 were kept in the Vichy Air Force, based in
Rabat, Casablanca and Morocco respectively. These groups had to
face the allied planes during the regrettable case "Mers El Kebir",
and raids of retaliation that followed. After the rallying to
the French Free Forces, the Curtiss H75 aging finish their career
in the schools of fighter, or in secondary missions.
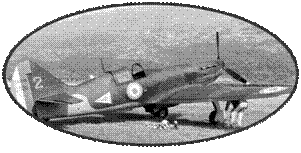
The final outcome
of the use of the Curtiss H75 during the Frances campaign is 275
sures victories and 96 likely for the loss of 35 pilots. Some
pilots will win numerous victories aboard this aircraft, such
as Edmond Marin la Meslee, the Aces of the French Aces with his
16 victories..
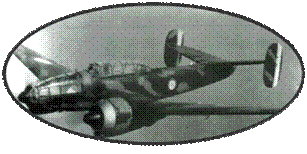
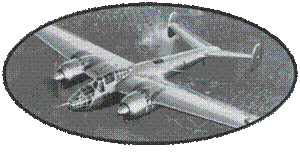
This aircraft was
appreciated by its pilots for its ease of piloting, its large
cokpit, and its general stability which made it a good platform
of shooting. On the other hand, its armament was far too weak:
4 machine guns of 7.5mm, 6 for the last versions, and its engine,
although reliable and robust, was not powerful enough. Its protection
was perfectible, including unprotected tanks.