|
Site in French
|
|
BLOCH MB152

Technical
Specifications
|
Type
|
Mono-seat Fighter
with low wings
|
Date first flight
|
Décembre
15, 1938
|
|
Wingspan
|
10,542m
|
Lenght
|
9,104 m
|
|
Height
|
3,960m
|
Wing Area
|
17.32m2
|
|
Empty Weight
|
2158Kg
|
Max. Takeoff Weight
|
2748 Kg
|
|
Cruising Speed
|
km/h.
|
Maximum Speed
|
510 km/h at4500m
|
|
Climbing Speed
|
4000m in 6mn 12s
|
Service ceilling
|
11050m
|
|
Range
|
540kms at5500m
|
Crew
|
1
Pilot
|
|
Motorization
|
1 Radial
Engine Gnôme & Rhône 14 cyl 14N49 de 1050ch
at 3600m
|
|
Armament
|
2x machine-guns
MAC 34 de 7.5mm in the wings
2x 20mm cannons Hispano Suiza HS-404 in the wings
|
|
|
750 Bloch of the MB 150 series have been built since the date of the first flight on May 4, 1937. They are divided into:
- 136
Bloch MB 151 with Gnome Rhône 14N35 engine: 25 for Greece, 30
for naval aviation, 85 for schools and 4 for SNCASO for testing
- 555
Bloch MB 152 broken down as follows :
- 203
aircraft with Engine Gnôme-Rhône 14N25 or 14N39
(Serial nb from 9 to 300)
- 352
aircraft with Engine
Gnôme-Rhône 14N49 (nb 301 to 431, nb
497 to 500 and nb 501
to 696 )
-
1
Bloch MB 153 : From cell no. 434
- 1 Bloch 154 with
Engine Wright 1820 from
cell no435
-
3 Bloch
MB 155 of pre-series : on the cells of Nos. 16,194 and 262
- 44
Bloch MB 155
with
Engine
Gnôme-Rhône 14N49 (No 701 à 744)
- 1
Bloch MB 157
To date, of the 743 aircraft manufactured, 541 are listed in the list below

In 1934,
the "C1" plan was launched for a single-seater fighter, which
stipulated that the new fighter should be able to fly at 450km
/ h. The machines presented by the various manufacturers are the
Loire 250, the Dewoitine 513, the Nieuport 161, the Morane 405
and the Bloch 150. The latter is equipped with a Gnome & Rhône
14Kfs radial engine of 14 Cyl. developing 900 Cv. This aircraft,
designed by the engineer Roussel and his team, presents on the
ground, a very picked look due to a compact landing gear.
The first tests were
not very glorious: the MB150 did not manage to take off on its
first flight, October 8, 1936 ... Its competitor Morane 405 having
been ordered in series, it was not until early 1937, that The
state was again interested in this project. It undergoes many
modifications: an enlarged wing surface, a new Messier train,
and a more powerful engine. This prototype MB150 n ° 01 flew on
September 29, 1937. Its behavior is judged globally healthy, but
its speed does not exceed 434km / h. It underwent a second wave
of modifications: increased span, enlargedrudder, unique radiator
placed between the legs of the train, and several engines were
tested to give the MB 152, MB153, MB154 (see chapter "versions").
25 pre-series aircraft are ordered, followed by another 450 by
the end of 1939. These orders form part of plan "V", intended
to supply 950 modern aircraft in one year.
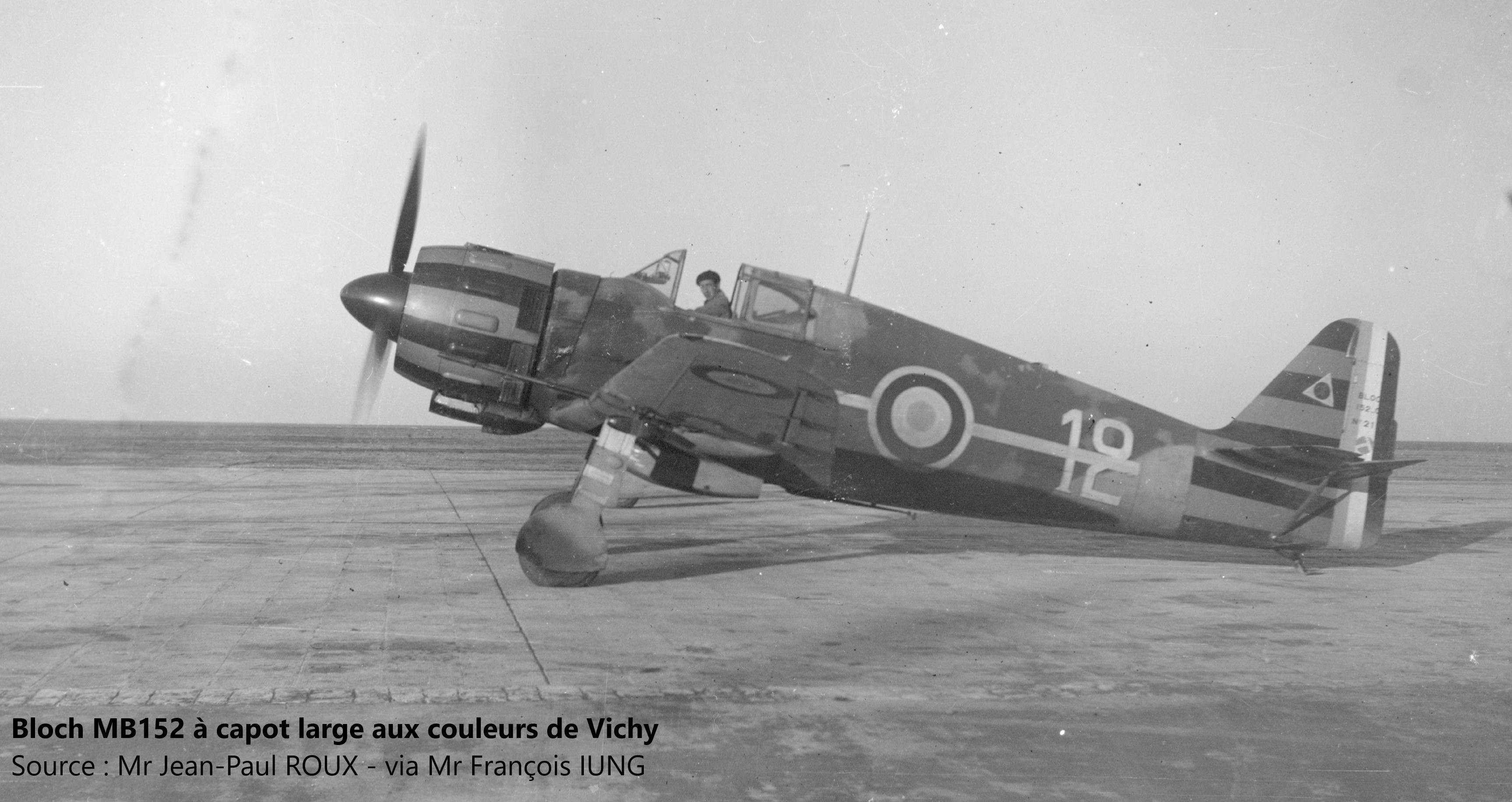
The Bloch MB150 proved very unsuitable for mass production. The modifications made: reduced wing area, new profile, reduced armament to 4 7.5mm machine guns, single radiator moved under the left wing, new GR14 N-11 engine of 920 Cv, gave birth to the Bloch MB151. Its first flight took place on August 18, 1938, and highlighted the major problem of the aircraft: engine cooling. The engine hood, which is very rugged, does not allow efficient cooling. While the MB151 continued to be produced, its replacement, the MB152 was born. On a cell of MB151, a 14 N-21 engine was grafted, and the armament modified in 2 guns of 20mm and 2 machine guns of 7.5mm. His first flight of December 15, 1938, showed that the problems of cooling were far from over. There followed a wave of various tests with hoods and cones of different diameters.
The production of the MB151 starts very slowly, a hood of a diameter mast is adopted on all the models: this improved the cooling, but penalized performances already unflattering. The Bloch MB151 is relegated to training, while the production of the Bloch MB152 follows its course with two different engines: either a GR 14 N-25 of 920 CV or a GR 14 N-49 of 1050 CV (See details production chapter). After a difficult start of equipment due to a lack of equipment, particularly propeller, the delivery of the Bloch MB152 accelerated and, at the end of the fighting, 632 Bloch 152 and derivatives were taken into account by the Air Force , Including 9 Bloch MB155.
This last version,
based on the MB152, is profoundly reworked (see chapter versions).
The first MB155 series was stolen on April 3, 1940, but only 10
out of the 400 ordered were completed before the Armistice. The
occupant nevertheless authorizes the construction of 19 cells
almost completed on the assembly lines.
The latest in the
family, the Bloch MB157 is built around the engine Gnome & Rhone
14 R-Meteor. This version is described on the page dedicated to
this aircraft.
The result of the
losses, at the end of the Battle of France, was 80 Bloch MB152
lost, 8 of which by accident, to which must be added 4 Bloch MB151
of which 2 lost per accident. The balance sheet of this aircraft
is 150 sures victories for 36 likely, which is far from negligible
given the superiority of the Luftwaffe.
The Bloch 152 remaining
after the Armistice have equipped the Fighter Groups maintained
in the Free Zone. Thus, during the invasion of the free zone by
the Germans in November 1942 after the disembarkation of the Allies
in North Africa, there were still nearly 300 aircraft of the series.
The Germans recovered about 180 for its training equipment, or
to equip its ally, Romania.
 |
The
MB 150 made its first flight on May 14, 1937 in Villacoublay.
The armament is composed of 2 20mm cannon and 2 machine-guns
of 7.5mm. After the first tests, he received a new Messier
train, his 14fs engine was replaced by a 14N07 which allowed
him to reach 434km / h. After the official tests at the CEMA,
the wingspan passes from 10.02 to 10.13m, the radiators of
wings are replaced by a central and receives a motor 154N-01
of 940 cv. New tests lead to new modifications: increase of
the surface of rudder, and more powerful engine: a 14N21 of
1030hp. Three prototypes were ordered in 1938, followed on
April 7, 1938 by 25 aircraft, and then a larger order of 450
machines ... This plan was never followed, and a new cell
was designed to allow rapid production by SNCASO: This gave
rise to MB 151-01 |
 |
The
main differences with the MB150 are: a span increased to 10m54
and a wing surface reduced to approx. 15m2 thanks to the reduction
of the rope, the adoption of a 14N11 870cv engine and a more
enveloping hood; A armament of 4 MAC34 of 7.5mm. The oil cooler
is installed under the wing. The first flight on 18 August
1938 in Villacoublay revealed from the start serious problems
of stability at high speed and cooling. In addition, the desired
480km / h was never reached, despite the adoption of different
types of flaps or tailplanes, both on the prototype and on
the standard versions, equipped with more powerful engines:
895cv. Cooling is immediately apparent as the weak point of
the aircraft, which will still limit already low performance. |
 |
The Bloch MB152 was
developed in October 1938, from the cell of No. 433. It
adopted a 14N-21 engine of 1030hp with which it was hoped
to reach 520km / h. Its armament is composed of 2 20mm cannons
and 2 MAC 34 machine-guns of 7.5mm. From the first flight,
on December 15, 1938, the same problem of overheating appeared,
limiting the speed to 480 km / h In 1939, many hood diameters,
from 0.75 to 1m were tested, but production being late,
Finally, in January 1940, the hood of 0.85m was adopted
definitively and the Bloch 152 received exhaust pipes copied
on the Curtiss H75. In addition, the cooling surface of
the oil cooler is increased to 8m². The engine for its part,
is a Rhone GNOME 14N49 driving a Chauvière propeller model
371
|
|
|
At
the end of October 1938, cell No. 434, received an American
engine Pratt & Whitney R19830 SC3-G "TWIN WASP" and a Hamilton
propeller. He made his first flight on 8th April 1939 in Villacoublay
and was then evaluated by the CEMA. Despite the modifications
made following the official tests, his performances were not
much better than those of the Bloch 152. A model 154 was envisaged
with a Wright Cyclone engine, but the engine did not arrive
in time ... |
 |
The
MB155-01 prototype was prepared from the cell of MB152 No.
449. It is distinguished from the MB152 by a more aerodynamic
nose, a cockpit moved backwards to insert a 720l tank and
a better protection of the windscreen. Its cannons are fed
by strips. The stabilizer loses its support mats, and the
engine is a Gnome-Rhone 14N49 of 1100hp. He makes his first
flight on December 3, 1939, and the first series aircraft
flew to Déols on April 3, 1940: if its performances are better,
they remain inferior to those of the best German aircraft.
Some aircraft were delivered in Squadron before the armistice
and two were destroyed on the ground on June 18th. |
 |
The
cell of the MB 157 was created around the engine Gnôme Rhône
14 R-4 of 1700cv with turbocharger 2 stages. The construction
began in December 39 in Villacoublay, but events slowed down
its development and its factory was bombed in June 1940. The
aircraft was evacuated to the south but was captured and transferred
to the SNCASO in Bordeaux where the plane was completed. The
first flight took place in March 42 and revealed a aircraft
with amazing performances: 710 km / h and only 11 minutes
to climb to 7900m ... |
Bibliography
|
1)
_ Editions LELA PRESSE ; Collection "Histoire de l'Aviation"
- Le Bloch MB 152
From
Serge Joanne

|
2)
_ Editions LELA PRESSE ; Collection "Les Ailes de la
Gloire"
- No3 :Bloch 150 / 151 / 152 / 155 / 157 et 700 C1
From
P. MARCHAND / J.TAKAMORI

|
Photos Album
- Sources Mrs Jean-Paul ROUX
et François IUNG
- Book : "Le
Bloch MB152 "
From Serge JOANNE - Editions LELA Presse
- Book : "No3
:Bloch 150 / 151 / 152 / 155 / 157 et 700 C1
"
From P. MARCHAND / J.TAKAMORI - Editions LELA Presse
- ...
|