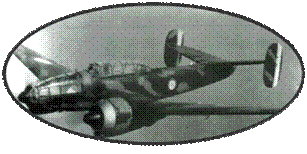
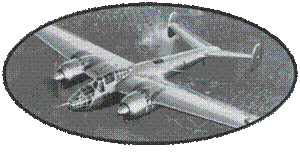
The Caudron
CR714 was conceived around the concept of the "Light Figher".
The CR714 is a direct descendant of the glorious record aircraft
of the brand. The first model C710 with fixed train, studied by
the team of Maurice DEVLIEGER, was presented in 1934, in response
to the program C1 (renewal of the fightert) in the category light
fighter. The C710, which flew for the first time on July 10, 1936,
was rejected because of its too limited performance: 460 km /
h in level. It is quickly followed by the CR713 "Cyclone". The
design is identical to the C710, this time it owns a retractable
gear and a redesigned drift. It flew for the first time in December
1937. Only Russia was interested in this CR713, as well as the
C710. (See chapter version)
Caudron continues the development
of the Caudron fighter, and presents the CR714, very similar to
the CR713, flying for the first time on July 6, 1936. The tests
continue (see chapter version) while the first orders arrive in
November 1938: 20 exemplary and 180 optional. The Air Force saw
in this aircraft a double interest: it did not use the Hispano
Suiza 12Y-31 engine of the D520 and MS 406 in particular, and
used non-strategic materials. It is mostly made of wood, with
a wing made of plywood and only a few Magnesium fairings are used
on the fuselage. The CR714 quickly revealed its major weaknesses:
sub-motorized, and weighed down by the latest military reinforcements
and equipment, its performance is mediocre, while its arming of
4 machine guns of 7.5 mm in the wings under fairings, is much
too weak. The Air Force decided to block the manufacture of the
90th aircraft, and to reserve part of the exemplary already manufactured
in Finland.
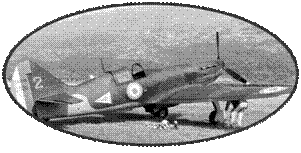
The delivery started slowly, with the commissioning of 9 aircraft in March 1940. Six of them were delivered to Finland which withdrew them from service in March 1941 ... This is one of them, N ° 5 (registered C-553), which after many journeys is being restored, and may be presented one day at the Museum of Air and Space
The CR714 were first assigned
to the DIAP (Polish Aviation Training Depot) and the GCMP (Polish
fighter and walking group) for training aircraft, before going
to equip the new GC I / 145 " Warsaw ". This group is initially,
assigned to the defense of Lyon, before being moved on the ground
of Villacoublay. In spite of problems of reliability, a lack of
qualified personnel and spare parts, the group aligned to May
24, 1940, about thirty machines including eight operational.
The Polish pilots were able to make the most of this poorly performing product. The speed of the CR714 did not allow them to catch up with the German bombers, but they managed to shoot down 8 enemy planes for the loss of 4 pilots. On the evening of June 11, 1940, there remained only 11 CR714 within the group, which finally perceived Bloch 152 and Morane 406.
Better motorized
versions have been studied but have not yet been put into service:
the Cr760, a transition aircraft equipped with an Italian Fraschini
engine, until the new Renault 626 engine is available. Described
in the "Versions" chapter.
When the Germans
grab the aircfield of Guyancourt, where its based the workshops
of the manufacturer, they seize about twenty plane which will
serve as lure on airfields. The units present in the Free Zone
will be reformed at the end of 1941.
The Caudron firm was known before the war for these magnificent racing planes, its prestigious pilots, of which Hélène Boucher, tragically disappeared, but Caudron 714 demonstrated that it was impossible to transform a "Racer" into a fighter plane. Military equipment weighs down the cell and penalizes performance: the concept of the light motorized fighter is a failure.