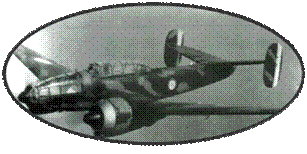
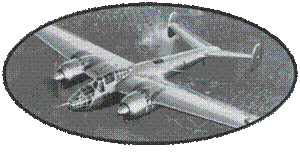
The Bloch
MB 135 was born from the program A21 of December 1936. This first
concerned a project of B4 twin-engined engines equipped with engines
Gnome Rhone (1934), program then extended to four-engines. The
Bloch MB 135 was in competition with the Breguet Br 482 or CAO
700, other four-engine.
The design
of the Bloch MB135 is linked to the Bloch MB131. The Bloch Company,
an integral part of the SNCAO after the nationalization of the
Aerospace Companies, tried to improve its Bloch MB 131, the main
shortcoming of which is the sub-motorization. The engines were
replaced by Hispano-suiza 14 AA and the aircraft became the MB133
with a double rudder. It only flew in 1937 and was followed quickly
by the Bloch MB134 quite similar. The study of this project stretched
out in time and the first of the three prototypes ordered did
not finally fly until July 1939. This rapid aircraft was damaged
in Avil 1940 during tests at the CEMA and was finally destroyed
before the German advance. In parallel with this project, the
Bloch company developed a four-engine derivative, a formula not
very common at the time, under the name Bloch MB135.
Only one
of the two prototypes was manufactured, equipped with Gnome-Rhone
14M engines, less powerful than the Gnome-Rhone 14P, but with
a narrower cross-section, the Gauge engines (Gnôme-Rhône 14M6)
rotating in the opposite direction than the Gnome -Rhône 14M7).
The Bloch
MB 135 makes its first flight to Villacoublay on January 12, 1939.
This aircraft was immediately high-performance and easy to maneuver,
but no orders are made by the state: the latter prefer to concentrate
on the Leo 451 twin-engine or Amiot 356