Faced with the inability
of the French industry to produce enough modern bombers, the Minsitère
de l'Air turned to foreign countries, especially the United States.
The French delegation is very impressed by the performance and
handling of the Douglas Model 7B. And despite the crash of a aircraft
in demonstration on an engine, France passes a first order of
100 copies on February 15, 1939. The first aircraft French, became
Douglas DB7, flew in the United States on August 17, 1939.
After France entered the
war, a second order of 170 aircraft passed in October 1939. The
latter are equipped with Pratt and Whitney S3C4-G engines with
compressors. But due to lack of availability of these new engines,
it was not until the 131st aircraft that the DB7 was equipped.
Two other commands will
have passed, but the Armistice will not allow to honor them. The
first dealt with 100 DB7A powered P & WR-2600 1600hp and the second
on 550 DB7-3 equipped with Wright R-2600-23.
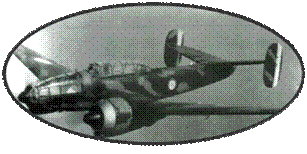
The Douglas DB7s delivered
to France were delivered by boat to Morocco and assembled on site.
They came out of the metal colored assembly lines before receiving
a standard camouflage. The first aircraft was seen by the Air
Force on 31 October 1939, but it was not until January 1940 that
they began to equip the Bombardment units. Manufacturing is slow,
however, and by May 10, 1940, only 64 units were in service.
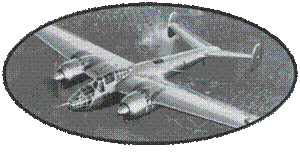
The Douglas DB7 took part
in the fighting only briefly: the first engagement took place
with GB II / 19 on 31 May 1940, and by 17 June all Douglas DB7
equipped bombers were sent back to North Africa . The Air Force
has decided to shelter in AFN its most modern equipment. During
this short campaign, 14 DB7 will be lost in combat.
In the end, only 116 aircraft
will have been received by the Air Force. 26 more will be assembled
after the Armistice, and 6 others will be used as spare parts.
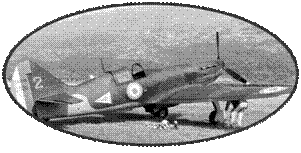
Under the colors of the
Vichy Army, the Douglas DB7 will be hired against the allies in
Gibraltar, before joining the French Free units. Some of them
will be used during the fighting for the reduction of the "pockets
of the Atlantic".