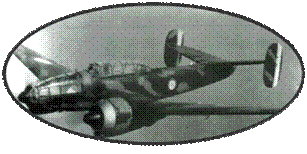
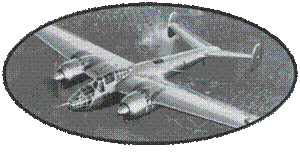
The Vickers Wellington's
design dates back to the 1930s. The Wellington fuselage is constructed
from grooved Duralumin beams, forming a huge latticework. It is
then covered with wooden rails on which is stretched a varnished
canvas. This process, used for the first time by Barnes Willis,
gives a very resistant structure. Many devices will thus return
to the base with the structure locally exposed, the outer fabric
having disappeared during a fire. This construction, however, involves
a significant manufacturing delay, compared to a traditional monocoque
construction
At the end of the 1930s,
80 Wellington a month will come out of Weybridge and Chester. After
the declaration of war, 300 devices a month will be produced at
the Weabridge, Chester and Blackpool sites.
The prototype made its first
flight on June 15, 1936 with J. Summers as pilot. The device was
validated by the Ministry of the Air on August 15, 1936 after having
undergone many modifications.
The Wellington Mk I, powered
by two 780 kW Bristol Pegasus engines, has a total of 180 units,
of which 30 are for the Royal New Zealand Air Force. The Wellington
Mk I entered service in October 1938 with the 9th squadron of the
RAF.
At the declaration of war,
183 Wellington Mk IA, improved turret version, equip the Royal Air
Force Bomber Command.
Wellington participated in
the first bombing of the RAF conflict on 4 September 1939 in Brunsbüttel,
Germany. The Wellington had the sad privilege of being the first
aircraft to be shot down on the Western Front, since two aircraft
will not return to the base that day ... The Wellington also participates
in the first night raid on Berlin August 25, 1940. Later, in 1942,
during the "1000 bombers" raid on Cologne on May 30, 1942,
599 out of 1046 aircraft were Wellington aircraft, 101 of which
were flown by Polish crews.
Wellington was commonly used
during the first two years. His record is eloquent: he carried out
47,409 missions, dropped 41,823 tons of bombs and ... 1,332 were
destroyed
Wellington's career will
end in Greece in 1944, with RAF support missions during the Greek
Civil War. Some devices will remain on site. The total production
is 11,461 copies.
Wellington was named "Wimpy"
by his crews, Wimpy being one of the characters of the cartoons
of Popeye.