Of the 50 aircraft ordered in the Netherlands by the French state, 40 were manufactured.
The first 4 aircrafts delivered in emergency, were equipped disaster
of the engine Hispano Suiza 14 AA 10. The following, equipped
with the good engine, the Rhone Gnome, were first delivered by
air, then, to simplify deliveries, Is decided to deliver the aircraft
dismantled by boat to the port of Le Havre, and then to assembly
to Nevers.
In fact, 40 Koolhoven were manufactured, but they remained in parts at Nevers. One of these 23 was finally completed.
In
total, only 14 aircraft were taken into account by the Air Force
which refused the first 4 delivered with a Hispano engine.
France, in 1938,
try to replace his outdated fighters. Given that the national
industry has not been able to fill the gaps itself, it is logically
towards the United States and the Netherlands that France turns
. England, for her part, is too busy modernizing herself to furnish
aircrafts outside the kingdom.
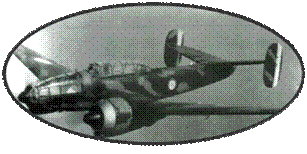
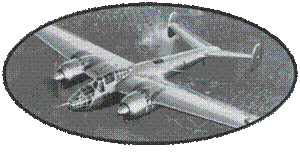
In the Netherlands, the company Fokker is already occupied with national orders (Fokker DXXI and Fokker G1) and only the company Koolhoven is ready to meet the French demand. The project of Koolhoven, called Model 1166, then FK 58 (58th model of the mark), is developed in only three months. The fuselage of the FK58 is made of steel tubes covered at the rear and covered with Duralumin plates at the front. The wings are classic, wood covered with plywood. The selected engine is a Rhône 14N39 Gnome of 1100 CV at take-off.
The prototype made
its first flight on July 17, 1938. The tests are conclusive and
a second prototype is launched quickly with slight modifications.
Serial production is planned before even having an official order.
The prototype is conveyed by air to France. It receives a civil
registration in order to allow it to fly over Belgium, still neutral
in October 1938. The tests at the CEMA of Villacoublay (Center
Experimentation of the Air Equipment) highlight a speed Low Maximum:
the 448 km / h reached are far from the 500km / h of the initial
specifications. The aircraft is however manageable and its time
of rise to 8000m is better than that of Morane MS406. The plane
is presented at the Air Show, with an advertisement for the least
optimistic. The official order finally passed in January 1939
for 50 aircraft to replace the Potez 25 in service in Indochina,
and equip two of the three fighter squadrons present in the Far
East.
The first 4 serial
deliveries delivered to the CRAS (Series Aircraft Reception Center)
are in fact equipped with Hispano-Suiza 14AA 10 engine with Dutch
civilian registrations. The following FK58s are first delivered
by air, the others to be delivered by boat and assembled at Nevers.
In December 1939, the situation was as follows: 40 FK58 were delivered,
and 23 were still parts in Nevers. Only one of them will be completed.
The Air Force also refused the first four FK58 equipped with Hispano-Suiza
engines. These engines, which are heavy, have a low output: 24.7
hp / liters compared to 30.5 hp / liters for the Rhône Gnome,
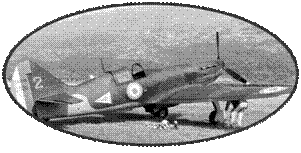
and thus degrade performance already very average ... So it received
14 troops allocated it to squadrons Of Defense, piloted mainly
by Polish pilots. Three FK 58 will serve as part of the Caen-Carpiquet
patrol, two other patrols based in Salon de Provence were equipped
with this poor fighter who fought until June 5, when they were
evacuated to Toulouse and Clermont-Aulnat
The survivors are
quickly frightened after the Armistice, and a exemplary is recovered
by the Germans.