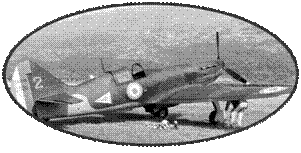
In early 1934, the Reich
Department of the Air (RLM) issued a tender for a light fighter.
The builders Heinkel, Arado and Focke-Wulf participated. Ehrard
Milch, at the head of the RLM is in cold with Willy Messerschmitt,
and it is only nine months later in March 1934, that the company
Messerschmitt was associated with the program.
Messerschmitt relied on the
experience gained with its modern single-engine Bf 108, to offer
a particularly relevant model all-metal: it retains a low-wing architecture,
with retracting gear and a closed cockpit. The first prototype took
off May 28, 1935 equipped with a Rolls-Royce Kestrel V engine with
a power of 695 hp. The flight was carried out without problem, except
for a train problem that forced him to land on his stomach.
The second prototype equipped with a 680 CV Jumo 210 engine was
presented at the 11th Olympiad in Berlin. The Bf 109 won against
his competitors. Only the Heinkel 112 resisted him and the Ministry
of Air ordered a small pre-series this also.
On the following prototypes,
many combinations of weapons were tried with first 2 machine guns
7.92mm on the hood, then a third between the cylinders to get closer
to the armament of the Spitfire then developing across the Channel.
This third machine gun is replaced by a 20mm gun, but this solution
generates severe vibrations. This weapon was replaced by two machine
guns in the wings, or two guns that will be mounted from version
BF109 E-3.
It was the JG 132 Richtofen
Squadron who received the first Bf109 B for experimentation in 1937.
Bf 109 B were also sent to Spain in the Condor Legion, and the German
pilots, after having tamed their machines, won the many successes.
On November 11, 1937, a special
BF109, equipped with a Daimler Benz engine pushed to 1660 hp, sets
a speed record with Dr. Hermann Wurster, factory pilot, at the controls:
610.95km / h.
The Bf 109 C was equipped
with a Jumo 210 G-1 injection engine (718 HP take-off). Its weaponry
consists of 4 machine guns of 7.92mm, then of 5 with the addition
of a weapon in the hub of the propeller. The BF109 C still used
during the Polish campaign will be removed from service at the end
of 1939. The Bf109 D that followed was very close to the C. It is
equipped with a Revi sight and its wing is reinforced to support
a higher mass.
The Bf109 E version was born
with the arrival of the DB 601 A (1100 hp) engines. This engine
required the lengthening of the fuselage of 25cm, and the nose radiator
split into a radiator under each wing. The propeller becomes three-bladed
metal. The engine is equipped with an injection system that allows
it to be powered regardless of the position of the device. This
will be a decisive advantage against his first opponents. The weaponry
includes 4 machine guns of 7.92mm on the version E1
On the E2 version, a 20mm
gun is again mounted in the propeller hub but unsuccessful: this
version will never be manufactured. The E-3 version retains the
2 hood machine guns, while the 2 wing guns are replaced by 20mm
guns. In this version, a slightly more powerful DB601Aa engine is
mounted.
The E-4 version is a reinforced
armor version around the driver. The canopy is modified for better
visibility. It will also receive the engine DB601N which develops
1200ch on takeoff. From this version will be extrapolated the E-4
variant equipped with a bomb thrower for 1 bomb of 250kg or 4 of
50kg
The E-5 and E-6 versions
are versions of unarmed reconnaissance of wings, equipped with cameras
Ultimate version of the E-series,
the E-7 which can receive a drop tank, thus remedying its main defect:
the low autonomy. externally; it is recognizable by its conical
propeller pan instead of truncated. The E-7 receives for the first
time a system of overpower "GM-1": for a few moments,
thanks to the injection of nitrous oxide, the engine is able to
deliver 250 to 380 additional ch 8000m.
Versions E-8 and E-9 are
reconnaissance versions based on Bf109 E-7
The Bf109 E also enjoyed
export success. Switzerland ordered 80, Yugoslavia 73 and Spain
44.
The aircraft has weighed
heavily since its first release: the 500 kg that separate the Bf109
B Bf 109 E make it less agile and manageable, but it is still a
formidable hunter. In total, nearly 4000 Bf 109 E, all variants
were produced before being replaced in early 1941 by the Bf109 F.
But this version and the following versions Bf109 G, Bf109 K and
BF 109 H are outside the scope of this site .